 Your HVAC system is the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning for your home all bundled into one unit. Most homes and offices use HVAC units because they provide an easy way to maintain a comfortable indoor environment all year long. Central HVAC is what most people want. It is considered best because of the convenience of functioning and also the reduction in the noise.
Your HVAC system is the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning for your home all bundled into one unit. Most homes and offices use HVAC units because they provide an easy way to maintain a comfortable indoor environment all year long. Central HVAC is what most people want. It is considered best because of the convenience of functioning and also the reduction in the noise.
HVAC systems have changed drastically over the years as technology has progressed and more efficient components have been put in place. These units range in size, capacity, and price – what you need will largely be based on the area of your home or office space and on any features you want. To keep the cost of these units at a reasonable level manufacturers have made some cost-effective solutions by considering energy consumption.
Let’s consider the different parts of an HVAC system:
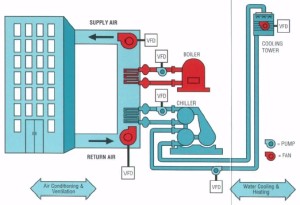
One of the largest components is the furnace unit. Whether in a home or office, you’ll usually find these installed in the basement or attic. It pushes hot or cold air out through the ducts that carry it throughout the rest of the building. Vents are placed throughout the ductwork, which allow the warm or cool air to pass into rooms and change their interior temperature.
The heat exchanger takes the cold outside air and heats it. There is one of these in every furnace. When the air enters through the duct it is quickly heated either by gas burners or electric coils depending on how the unit functions. The evaporator coil is much the same only it cools hot air coming in from outside. Evaporator coils are connected to the HVAC system’s condensing unit, which is typically located on the exterior of the building.
Separate from the furnace, the condensing unit is usually installed outside the building. This unit is directly connected to the evaporator coil. It uses refrigerant to create a chemical reaction that absorbs heat so the furnace will blow cool air through your building. Refrigerant lines are metal tubes that carry the refrigerant liquid to the evaporating coil and return the gas to the condensing unit. Refrigerant lines are usually made from aluminum or copper. They are designed to be durable and functional under extreme temperatures.
The thermostat is directly connected to the furnace. Using temperature-sensing technology it will trigger the system when it gets either above or below a certain temperature. It is usually located in a central location accessibly by people. You can have more than one thermostat connected to a system; many people have dual zone controlled homes and have a thermostat both upstairs and downstairs.
Ducts and vents are the final piece of the system. They are usually put in as the building is being constructed and run through the ceiling. The ducts carry the air and the vents cut into them distribute it.
